|
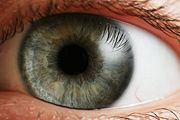
All knowledge enters through the eye….
The eye is the tree in the garden in Eden…
The eye produces the fruit of the tree…
The eye plugs the fruit and the brain eats
what the tree produce…
Gen. 3: 6; and when the woman saw that the
tree was good for food and that it was pleasant to the eyes, and a tree to be desired to make one wise,
she took the fruit and did eat and also gave to her husband (spirit/brain) and he did eat.
AND THE EYES OF THEM BOTH WERE OPENED AND
THEY KNEW…(they received knowledge.)
THE EYE IS THE MOST IMPORTANT TOOL OF CREATION.
without the eye you wouldn't know; what you smell, hear, feel, taste.
New Creation Of Heaven And Earth
CHAPTER 1
All quotations are from the King James
Version 1611.
New Creation Of Heaven And Earth
The Bible is one of the most discussed
books on earth today. People “kill” each other and also love each other because of the Bible.
Then there is the difference in beliefs
between the parties about evolution and creation.
Some people rejects scientists theories
that states that life started by way of evolution, and believe strictly that “God” created everything.
I can’t really understand this ongoing
battle because to my mind evolution is also a way of creating.
The way I think about evolution is “advancing”
from a previous creation. Is it not true that technology advanced dramatically from a 100 years ago?
Rock became steel by way of knowledge
and steel advanced to airplanes. Telephones to cell phones, radios to satellite television and so on and so on…
The Internet is helpful to advance human
knowledge, to share knowledge and nothing seems to be impossible any more. The angels learn from us.
The visible things although visible to
us are of less importance. Eternal life is more important… spirit, life and eternity are more valuable. Not evolution
as in theory but creation for a better eternal future.
Does it really matter where you come from?
Or is it of greater importance what lies ahead of us? Fact is, the human mind, intelligence, empathy ( we are no longer barbaric)
and ability advanced through time and this is true evolution without contradicting theory. Just think what this could mean
to your spirit….
According to the scriptures, God is spirit,
and everything you know has spirit within it, otherwise it could not be alive. Let’s take for example plants. Plants
must have spirit otherwise it would be lifeless and will not grow. For this reason then “the spirit in the plant or
animal” could wish to change. This could be for an array of reasons, for instance to defend itself, or to become more
attractive.
Is it therefore the plant or animal you
see that brings the change? Or is it the spirit (God) in the plant that brings forth the change?
Well this is true, unless you believe
that God is not in everything, and therefore everything would be dead because we all know God = life, all forms of life. However
the bible is clear that God is in everything. You can decide if you believe the bible but we will discuss it in detail.
Creation is a slow process, or at least
in the mind it is…
Then there is the question: Did God create
everything in just 6 days (144 hours)?
We can’t be that naďve to think
and believe that this could be true. If this was true, why does a human take 18 or 20 years to reach adulthood or trees years
to become big and provide shade? Why doesn’t it then take only 0,003 seconds for instance?
Genesis is in its whole a book of symbols;
if you don’t believe this you would understand nothing about this revelation looking through the seventh eye. If you
don’t believe this it would be easy to get rid of Satan because then you believe that it was a real snake that
seduced Eve, and all we have to do is to kill all the snakes and Satan will be DEAD.
Genesis is also a summary of the bible.
We are on earth to gain knowledge. After
all, we eat from the tree called knowledge. And what’s more? We also die because we eat from the tree of knowledge Gen
3:3 and 6.
Knowledge has improved significantly over
the years, especially referring to the last hundred or so years, purely because we eat of the tree of knowledge.
If you think back at the prehistoric world,
there was a time when we believed the earth was flat. Now we know that the earth is spherical. Thus we are still receiving
knowledge everyday, for we still eat from that tree of knowledge.
There is a big difference in believing
something or to have knowledge about something.
Have you ever thought about the following:
God created the human (Adam & Eve) on the sixth day, but it is still the sixth day. It cannot yet be the seventh day,
for the seventh day is a day of rest and you are supposed to enter the day of rest. See Revl. 14: 13 and Psalm 95: 11. Or
are you already in the future eternity…
God only completed the creation at the
end of the sixth day. And because we are still in the sixth day, God has not yet completed the creation. Gen 1:31.
Gen.2: 1; thus the heavens and the earth
were finished and ALL the host of it. It must be clear from this script that the entire creation were finished on the sixth
day, however, God is still busy creating earth (all visible things) and heaven (the invisible.)
It is quite clear from the photos below
which show the birth of stars that God still hasn’t finished the creation and this is indisputable evidence that we
are still on the sixth day of creation.
Spectacular star birth pictures on Hubble’s 17th birthday
The Bible is one of the most discussed
books on earth today. People “kill” each other and also love each other because of the Bible.
Then there is the difference in beliefs
between the parties about evolution and creation.
Some people rejects scientists theories
that states that life started by way of evolution, and believe strictly that “God” created everything.
I can’t really understand this ongoing
battle because to my mind evolution is also a way of creating.
The way I think about evolution is “advancing”
from a previous creation. Is it not true that technology advanced dramatically from a 100 years ago?
Rock became steel by way of knowledge
and steel advanced to airplanes. Telephones to cell phones, radios to satellite television and so on and so on…
The Internet is helpful to advance human
knowledge, to share knowledge and nothing seems to be impossible any more. The angels learn from us.
The visible things although visible to
us are of less importance. Eternal life is more important… spirit, life and eternity are more valuable. Not evolution
as in theory but creation for a better eternal future.
Does it really matter where you come from?
Or is it of greater importance what lies ahead of us? Fact is, the human mind, intelligence, empathy ( we are no longer barbaric)
and ability advanced through time and this is true evolution without contradicting theory. Just think what this could mean
to your spirit….
According to the scriptures, God is spirit,
and everything you know has spirit within it, otherwise it could not be alive. Let’s take for example plants. Plants
must have spirit otherwise it would be lifeless and will not grow. For this reason then “the spirit in the plant or
animal” could wish to change. This could be for an array of reasons, for instance to defend itself, or to become more
attractive.
Is it therefore the plant or animal you
see that brings the change? Or is it the spirit (God) in the plant that brings forth the change?
Well this is true, unless you believe
that God is not in everything, and therefore everything would be dead because we all know God = life, all forms of life. However
the bible is clear that God is in everything. You can decide if you believe the bible but we will discuss it in detail.
Creation is a slow process, or at least
in the mind it is…
Then there is the question: Did God create
everything in just 6 days (144 hours)?
We can’t be that naďve to think
and believe that this could be true. If this was true, why does a human take 18 or 20 years to reach adulthood or trees years
to become big and provide shade? Why doesn’t it then take only 0,003 seconds for instance?
Genesis is in its whole a book of symbols;
if you don’t believe this you would understand nothing about this revelation looking through the seventh eye. If you
don’t believe this it would be easy to get rid of Satan because then you believe that it was a real snake that
seduced Eve, and all we have to do is to kill all the snakes and Satan will be DEAD.
Genesis is also a summary of the bible.
We are on earth to gain knowledge. After
all, we eat from the tree called knowledge. And what’s more? We also die because we eat from the tree of knowledge Gen
3:3 and 6.
Knowledge has improved significantly over
the years, especially referring to the last hundred or so years, purely because we eat of the tree of knowledge.
If you think back at the prehistoric world,
there was a time when we believed the earth was flat. Now we know that the earth is spherical. Thus we are still receiving
knowledge everyday, for we still eat from that tree of knowledge.
There is a big difference in believing
something or to have knowledge about something.
Have you ever thought about the following:
God created the human (Adam & Eve) on the sixth day, but it is still the sixth day. It cannot yet be the seventh day,
for the seventh day is a day of rest and you are supposed to enter the day of rest. See Revl. 14: 13 and Psalm 95: 11. Or
are you already in the future eternity…
God only completed the creation at the
end of the sixth day. And because we are still in the sixth day, God has not yet completed the creation. Gen 1:31.
Gen.2: 1; thus the heavens and the earth
were finished and ALL the host of it. It must be clear from this script that the entire creation were finished on the sixth
day, however, God is still busy creating earth (all visible things) and heaven (the invisible.)
It is quite clear from the photos below
which show the birth of stars that God still hasn’t finished the creation and this is indisputable evidence that we
are still on the sixth day of creation.
Spectacular star birth pictures on Hubble’s 17th birthday
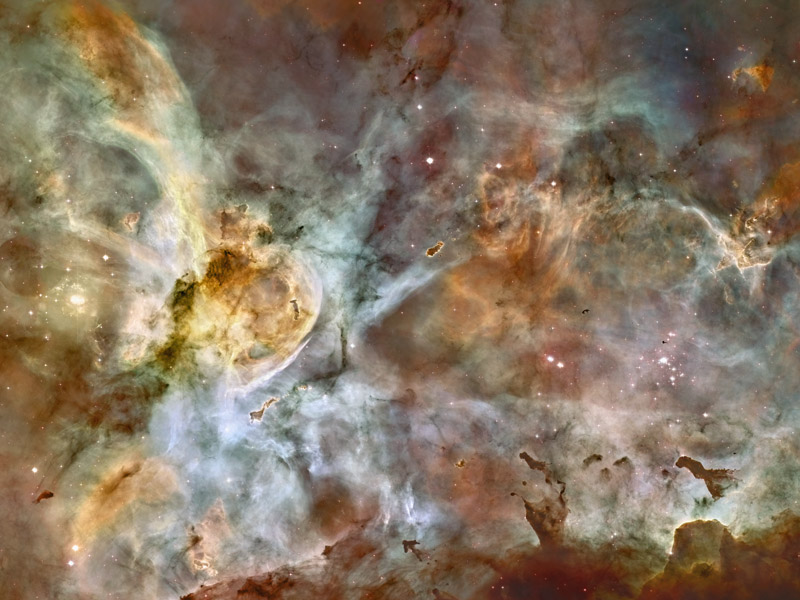

Panorama of the Carina Nebula
24 April 2007
A 50 light-year-wide view of the Carina Nebula has been released to celebrate the 17th
anniversary of the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope.
Carina is an immense nebula
situated at an estimated 7 500 light years away in the southern constellation Carina, at the keel of the ship Argo Navis.
This panoramic image of the nebula gives us a peek into star formation as it commonly occurs along the dense spiral arms of
a galaxy.
Think about this for a minute: Gen 2:17
of the tree of knowledge of good and evil, thou shalt not eat of it, for in the day thou eatest thereof thou shalt surely
die.
It says: the same day you eat the fruit
of this tree of knowledge, that same day you will die. This “same day” being the sixth day.
You might now differ and say; the sixth
day is the day on which God created the human and that day is long gone. For those I ask a question; Adam ate the fruit on
the sixth day and God said; the same day you eat the fruit, that same day you will die; my question is; why did Adam
lived another 800 years and didn’t die on the same day?
The answer is; simply because it is
not yet the end of the sixth day.
If the creation came to an end, or was
completed on the so-called sixth day, why is it that there is still the birth of stars at this moment? (The expanding universe= the proof)
At the same time, we are
not yet in the day of rest. The good news however is that it is in the near future, that is if you understand this revelation.
If you don’t believe this TRUTH,
the bible will be a lie and a sealed book to you.
What’s more, the human was created
to live for only one day, which is the sixth day. At the end of the sixth day humans and everything you know and see will
“disappear” forever…
Why you may ask? Because we then move
over to the seventh day, the day of rest, the day where you will receive a new body, for the body you now know will disappear,
be demolished Gen 2:1-3, 1Cor 15:52
At this moment we are less than one hour
away from this happening. One hour representing 41,666 years in biblical formula. Also equaling one generation.
Did you hear? In less than 40 years (by
now) everything that you see would have changed, including your body. This is the so-called second coming!!
What does the bible say about how everything
came into being?
To really understand this discussion you
will have to read the full manuscript namely this revelation of Johannes.
Never the less, lets move on to Gen 1,
the creation of the universe (heaven and earth)
Under the term “heaven” we
must conclude: all of what we call space. And under “earth” all visible heavenly bodies, stars, planets, moons
and suns.
If we look at the order of creation, as
stated in the bible, we will see that the order doesn’t make sense.
The logical order of creation would be
as follows:
Day 1:
God said let there be light. (the Big Bang, fertilization, new life in the first dimension of evolution * see my definition
of evolution*
Day 2: (day 4 according to the Bible)
Forming of the planets sun and stars.
Day 3: (day 2 according to the Bible)
God created the atmospheres around the planets and stars
Day 4: (day 3 according to the Bible)
Dry land appears. Plants start to grow, also in the water.
Day 5: Creation of the sea creatures and
birds
Day 6: Creation of land creatures (animals
and humans)
Day 7: human and all flesh disappear,
the rest of God (you and me)
According to the Bible, trees and plants
were created on the third day, but the sun was only created on the fourth day. Now we all know that plants need photosynthesis
from the sun to grow. See below;
Evolution on Earth
See also: History of Earth

Atmospheric
gases scatter blue light more than other wavelengths, giving the Earth a blue halo when seen from space.
The history
of the Earth's atmosphere prior to one billion years ago is poorly understood and an active area of scientific research. The
following discussion presents a plausible scenario.
The modern
atmosphere is sometimes referred to as Earth's "third atmosphere", in order to distinguish the current chemical composition from two notably different previous compositions. The original atmosphere was primarily helium and hydrogen. Heat from the still-molten crust, and the sun, plus a probably enhanced solar wind, dissipated this atmosphere.
About 4.4
billion years ago, the surface had cooled enough to form a crust, still heavily populated with volcanoes which released steam, carbon dioxide, and ammonia. This led to the early "second atmosphere", which was primarily carbon dioxide and water vapor, with some nitrogen but virtually no oxygen. This second atmosphere had approximately 100 times as much gas as the current atmosphere, but as it cooled much of the carbon dioxide was dissolved in the seas and precipitated out as
carbonates. The later "second atmosphere" contained largely nitrogen and carbon dioxide. However, simulations run at the University
of Waterloo and University of Colorado in 2005 suggest that it may have had up to 40% hydrogen.[6] It is generally believed that the greenhouse effect, caused by high levels of carbon dioxide and methane, kept the Earth from freezing.
One of
the earliest types of bacteria was the cyanobacteria. Fossil evidence indicates that bacteria shaped like these existed approximately 3.3 billion years ago and were the first oxygen-producing
evolving phototropic organisms. They were responsible for the initial conversion of the earth's atmosphere from an anoxic
state to an oxic state (that is, from a state without oxygen to a state with oxygen) during the period 2.7 to 2.2 billion
years ago. Being the first to carry out oxygenic photosynthesis, they were able to produce oxygen while sequestering carbon
dioxide in organic molecules, playing a major role in oxygenating the atmosphere.
Photosynthesising plants would later evolve and continue releasing oxygen and sequestering carbon dioxide. Over time, excess carbon became locked in fossil fuels, sedimentary rocks (notably limestone), and animal shells. As oxygen was released, it reacted with ammonia to release nitrogen; in addition, bacteria would also convert ammonia into
nitrogen. But most of the nitrogen currently present in the atmosphere results from sunlight-powered photolysis of ammonia released steadily over the aeons from volcanoes.
As more
plants appeared, the levels of oxygen increased significantly, while carbon dioxide levels dropped. At first the oxygen combined
with various elements (such as iron), but eventually oxygen accumulated in the atmosphere, resulting in mass extinctions and further evolution. With the appearance of an ozone layer (ozone is an allotrope of oxygen) lifeforms were better protected from ultraviolet radiation. This oxygen-nitrogen atmosphere is the "third atmosphere". 200 – 250 million years ago, up to 35 percent of the atmosphere
was oxygen (bubbles of ancient atmosphere were found in an amber).
This modern
atmosphere has a composition which is enforced by oceanic blue-green algae as well as geological processes. O2 does not remain naturally free in an atmosphere, but tends to be consumed
(by inorganic chemical reactions, as well as by animals, bacteria, and even land plants at night), while CO2 tends
to be produced by respiration and decomposition and oxidation of organic matter. Oxygen would vanish within a few million years due to chemical reactions and CO2 dissolves
easily in water and would be gone in millennia if not replaced. Both are maintained by biological productivity and geological
forces seemingly working hand-in-hand to maintain reasonably steady levels over millions of years (see Gaia theory).
The universe/earth exists out of two “halves”
namely; heaven, and earth/soil the other half.
Heaven acts as male and earth as female,
the womb or soul of the universe. Thus earth is the mother of all life. This subject is discussed in another chapter of “this
revelation of Johannes (John)”
Please don’t compare this revelation
with any other religion of our time. There is diversity in different religions and that is healthy, it brings us together
and each and every religion has its purpose and all of us work for ONE BODY.
The meaning of the word Genesis is origin,
and thus the book Genesis must explain how everything came to be.
Scientists have it that 20 billion years
ago, creation (as we know it today), started off with the so-called Big Bang. Some scientists now draw the line forward to
about 15 billion years ago. Some scientists even suggests that the creation is only 13,7 billion years old.
Figures play a big role in the deciphering
of the symbols of the Bible, and 15 billion years doesn’t fit in.
The following appeared on a website;
The
British team was the first to analyse Hubble's Ultra Deep Field (HUDF) images, which provide mankind's deepest optical view
of the Universe. The team viewed the number of star-forming galaxies and found that there were far less than expected. The
rate at which new stars were born was a lot slower than formerly thought.
Scientists
believe that the energy released when stars were born provided enough radiation to lift a curtain of cold, primordial hydrogen
that formed after the Big Bang, now scientists are having to re-think that theory.
"We
can measure how fast stars are being born in the early universe," said Dr. Andrew Bunker. "But our results reveal a puzzle;
the birth rate seems low compared with more recent pasts. This is not what theorists had expected: at early times, the Universe
seems to undergo a rapid heating. The main candidate for what caused this is ultraviolet radiation, which can be generated
as stars are born. Our results suggest this was not the case, the small number of star forming galaxies found in the Ultra
Deep Field may not be sufficient to do this. Perhaps this heating happened further back in time, closer to the Big Bang."
By
analysing pictures taken by the Hubble telescope Bunker's team could see almost to the beginning of time. They were able to
identify 50 objects likely to be galaxies so far away that light from them has taken 13 billion years to reach the earth.
The galaxies uncovered by the team existed 95 percent of the way back to the beginning of time. This is the closest man has
ever come to the Big Bang, when the Universe was less than a billion years old.
End
of quote.
If the light has taken 13
bl years to reach us then the universe must be much older than the + or – 13 bl years some scientists say. It must be
at least 6 bl years older which bring us to apr 20 bil.
Lets say the present creation is 20 billion
years in existence; now divide 6 creation days into 20 billion years. You’ll find that each day equals 3,333 billion
years.
Let us now discuss these days.
We will give you the Hebrew meaning of
the relevant words.
Day 1 Gen 1:1 in the
beginning God created the heaven and the earth.
*The conclusion is that he created two
separate “places” namely: a spiritual place and a physical place or an invisible place and a visible place.
Verse 2; and the earth was without
form and void.
Void meaning: to be empty, hollow, vacuity,
emptiness, tremble inward, palpitate, suddenly agitated, glisten, shining (white or red marble) a ruin.
*From this we can conclude: it was a vacuity
that became unstable/agitated/the gathering of waste. We can probably say that the vacuity was “sucking in” the
tiny visible components of the universe.
Without form: waste or desolation –
worthless.
*The “earth” at that stage
was without form because of the instability, the palpitation, and the agitation of this matter creating an abyss, a hurricane,
or a tornado. (See spirit below)
Also it became worthless. We discuss this
in another chapter.
Verse 2 cont: and darkness was upon
the face of the deep
Darkness: (Hebrew meaning;) enhanced darkness,
misery, destruction, death, sorrow, dark night, and obscurity.
*Enhanced darkness = to become more and
more visible/fossilized.
*This gathering of matter became more
and more dense, obscured and visible (not transparent) we can conclude that the visible is called darkness a place
of misery and sorrow.
Face: the part that turns namely these
“turning” masses that gathered.
Deep: an abyss, a surging mass, to make
an uproar, to agitate greatly, destroy, move, make a noise, to ring again, a pat
*This describes a boiling mass reaching
a point of explosion, making great noise/an uproar. (it will be impossible for us to even imagine or describe this noise.)
If we now rephrase the following; darkness
was on the face of the deep, we could perhaps read it as follow; this turning abyss became more and more visible, but did
not had any specific form yet, logically.
Verse 2 cont.: and the spirit of God
moved upon the face of the waters
Spirit: (Hebrew) wind, breath, air, anger,
smell, violent, by resemblance spirit or a tempest. The meaning of spirit in the New Testament hasn’t the same meaning.
*This violent tempest/hurricane is called
the spirit of God. This tempest was the result of this turning abyss. From this we can conclude that there had to be a previous
universe that “broke up” or were “sucked in” to become very dense or small and by way of the Big Bang
created the current universe. This “sucking” has dense the “material” to a state where it “exploded”.
Read below;
New discoveries about another
universe whose collapse appears to have given birth to the one we live in today will be announced in the early on-line edition
of the journal Nature Physics on 1 July 2007 and will be published in the August 2007 issue of the journal's print edition.
Researchers Look Beyond the Birth of the
Universe
User rating: 4.7 /
5 after 182 vote(s)
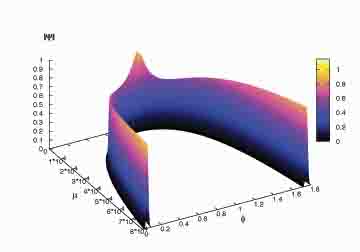
connects the former collapse
with the current expansion.”
The figure represents our expanding universe
as the right branch of the arc. Our time now is located at the 1.8 grid mark on the right side of the drawing. According to
Ashtekar's team's calculations, when looking backward throughout the history of the universe, 'time' does not go to the point of the Big Bang but bounces to the left branch of the drawing, which describes a contracting universe. Singh
explains, "The state of the universe depicted by its wavefunction is shown in space (\mu) and time (\phi). The big bang singularity
lies where space vanishes (goes to zero). Our expanding phase of the universe is shown by the right branch which, when reversed
backward in time, bounces near the Big Bang to a contracting phase (left branch) and never reaches the Big Bang."
According to Einstein’s
general theory of relativity, the Big Bang represents The Beginning, the grand event at which not only matter but space-time
itself was born. While classical theories offer no clues about existence before that moment, a research team at Penn State
has used quantum gravitational calculations to find threads that lead to an earlier time.
“There are two classical
branches of the universe connected by a quantum bridge. This connects the former collapse with the current expansion.”
The universe in its current
state is in an anti clock spin, the same as a tornado or the tornado that formed this creation. Also everything in our solar
system spins anti clock wise. This symbolize that we went back in time.
Somewhere in future the
universe will change into a clock wise spin.
See photo below;

Star Nursery
Photograph by G. Fritz Benedict, Andrew Howell,
Inger Jorgensen, David Chapell (University of Texas), Jeffery Kenney (Yale University), and Beverly J. Smith (CASA, University
of Colorado), and NASA
A merry-go-round of young stars flashes around the center of galaxy
NGC 4314. This spectacular close-up from the Hubble Space Telescope reveals the basic structural elements of a galaxy. At
the center glows a dense cluster of old stars, their mature status indicated by temperatures in the yellow and white part
of the spectrum. Even deeper into the center probably lurks an invisible black hole, common to most galaxies. A black hole
is matter so densely compacted that even light can't escape.
New stars usually appear in the spiral arms of a galaxy. But in this case the young, ultra-hot stars (blue and purple)
have formed in a ring, created when clouds of gas collapse into superdense cores. Ten times hotter and one million times
brighter than our sun, these new stars will eventually cool down and resemble the older stars near the center. Clouds of dust
and gas fog the edges of the image. Even farther out lies the unseen weave of dark matter, whose gravitational force
keeps the galaxy's hundreds of billions of stars bound together.
Scientists had discovered
a milky way that spins clock wise. Unfortunately those who placed the photo here had put the negative image and now it also
seems if it spins anti clockwise.
Spiral Galaxy NGC 4622 Spins "Backwards"

Note; Although it says it
spins backwards it doesn’t spin backwards but forward like a clock.
Photo is a negative; this
photo spins anti clockwise instead of clockwise.
Face: the part that turns (the abyss)
Water: the meaning of water in this respect
is; a fountain or an eye, which clearly describes this turning boiling/whirlpool masses. We are used to call the center of
a hurricane the eye.
Verse 3: and God said, let there be light.
And there was light
This violent tempest, this turning boiling
mass, called spirit, exploded. This describes the so-called Big Bang of 20 billion years ago.
Light: to set on fire, to cause or make
luminous.
This “abyss”, this turning
tower of masses, fell over from north to south and “burst open” in the midst according to the bible.
You now may argue and say that The Spirit
of God is not a tempest. (You might now think about the voice of the LORD God while walking in the garden in the cool of the
day, well this was much later. Think about what happened here.)
My friend, God has more than “one
side” and has different “powers”. In fact the bible says God has 7 different spirits. This is discussed
in detail in another chapter.
Verse 4: God saw the light that it was
good, and God divided the light from darkness
As we explained; before this explosion,
“space” became obscured (enhanced darkness the bible says) and “milky” because of the visible matter
floating in space and gathered as worthless material. After this explosion, these
milky particles were forming visible objects (planets, stars and sun) to leave the space “clear as water”. This
is the temporary division.
I say; the division is the separation
of the visible particles from the “air”.
And God called the light day and the darkness
he called night
He called the “cleared” space
light or day (transparent) and he called the visible objects darkness or night. Although you now see the sun as visible light,
the sun acts as the element that gives life, energy and even sperm to impregnate the earth/visible/female.
Read below;
Hubble Finds Evidence for Dark Energy in
the Young Universe
Scientists using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have discovered that dark energy is not a new constituent
of space, but rather has been present for most of the universe's history. Dark energy is a mysterious repulsive force that
causes the universe to expand at an increasing rate. Investigators used Hubble to find that dark energy was already boosting
the expansion rate of the universe as long as nine billion years ago. This picture of dark energy is consistent with Albert Einstein's prediction of nearly a century ago that a repulsive

15 May 2007
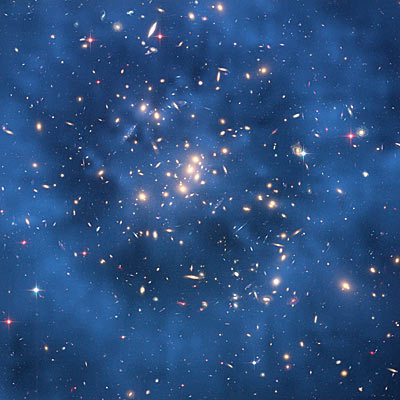
A team of astronomers used the Hubble Space Telescope to find the best evidence
yet for the existence of dark matter, present in the form of a ghostly ring in a galaxy cluster.
The ring had formed long ago during a titanic collision between two massive galaxy clusters.
The team’s discovery,
to be published on 1 June 2007 in the Astrophysical Journal, represents the first record of dark matter distribution that
differs substantially from the distribution of ordinary matter.
|
|
Hubble sees dark
matter ring in a galaxy cluster
|

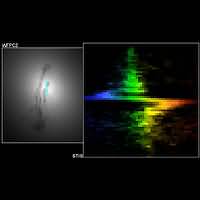
The colorful "zigzag" on the right is not
the work of a flamboyant artist, but the signature of a super-massive black hole in the center of galaxy M84, discovered by
the Hubble telescope's imaging spectrograph.
The image on the left, also taken by Hubble,
shows the core of the galaxy where the suspected black hole dwells. In a single exposure, astronomers mapped the motions of
gas in the grip of the black hole's powerful gravitational pull by aligning Hubble's spectroscopic slit across the nucleus.
During our discussions you will learn
how important it is “to know” that God calls the visible darkness.
God called the heaven light or
day and the visible earth darkness or night
Now we are at the end of day one or past
period 3,333 billion years in creation.
Day 2 Verse 6: God said, let there be a firmament in the midst of
the waters, and let it divide the waters from the waters.
Waters: different heavens (atmospheres)(spirits)
we discuss it in another chapter of this manuscript. (Noah’s ark that had three story’s, in fact symbolizes three
different heavens) We can conclude that the heavens are called “waters.”
“Atmospheres” form around
the “planets”. A dome (firmament) forms between these atmospheres, which seals in each atmospheres own spirit
or atoms, impenetrable from each other. (See Noah’s ark) A division was put in between the spirit of the planets and
the spirits of the heavens above (the interplanetary).
See sketches below;
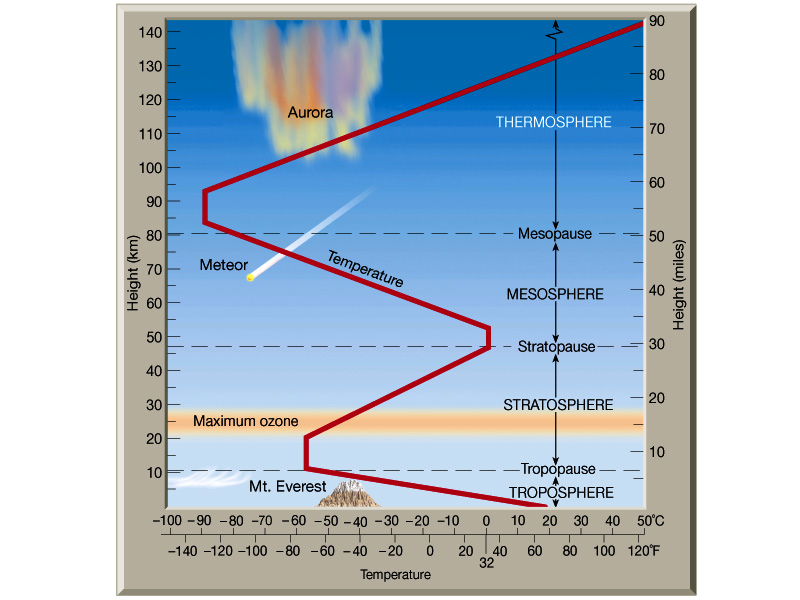
Verse 8: and God named the firmament heaven.
(Or different layers of the atmosphere) the word firmament also has the meaning of; to expand.
Water: spirit or heaven = transparent
substance or clear substance.
Day 3
The logical creation order now brings
us to verse 14 (6,666 billion years after the Big Bang) God said: let there be lights in the firmament of heaven to divide
the day from the night and let them be for signs and for seasons, and for days and years.
“We” move into a time zone,
whereas previously it was timeless. Further; gasses started to gather, collect and compacted together and started to “light
up” like the sun. Others like the moon, acted as mirrors, reflecting light.
A Very Big Bang
Patricia A. Mondore, M.A. and Robert J.
Mondore
"By the word of the LORD were the heavens
made...For he spoke, and it came to be; he commanded, and it stood firm" Ps. 33:6,9
Verse 16: God made two great lights; the
greater light TO RULE the day and the lesser light TO RULE the night, he also made the stars.
*Sun as energy in the day.
*Moon as energy for sleep, both needed
for growth.
It is clearly stated; to rule.
The meaning of to rule is; to have dominion
or to have power.
We can conclude that the sun and moon
played a big role in creation during this time for they have dominion.
Verse 17: God set them in the firmament
of the heavens to give light upon the earth.
Light; light in this respect means; light as an element or cheerfulness.
This firmament is in itself a “mirror”
reflecting everything in a “reversed” image, past image, a false creation to “keep us away”.
The universe doesn’t at all look
the way you see it. Think about this: if there was a Big Bang that has changed the universe 20 billion years ago, then the
following possibilities could well be true…
When you see a star “explode”
it could have happened millions of years ago but you only see a flash of it now, because we are bound to time in the form
of light years. The Hubble telescope sends picture from a spacecraft to earth about things that happened many light years
ago. Imagine seeing for the first time the light of a “new born star”
in the night sky, and the particular light has taken 10 billion years to reach earth, then:
It could have been totally transformed
by now.
It might have already burnt out or ceased
to exist (in other words by the time you see the light of a new star, that same star could already cease to exist for perhaps
10 billion years.)
if you perhaps use the following hypothesis;
you could perhaps have a telescope where you can now at this moment “see” this planet with even moving creatures
on it although it doesn’t exist for the past 10 billion years, because the light only now reach you.
We are “caught” in such a
situation here on earth.
I say; “we don’t exist,”
we are caught in the past.
This might be a bit too much for our brains
at this stage.
Scientists say that they now already
have photos of the universe of how the universe looked shortly after the Big Bang.
You have seen some of them here. Now what does that tell you?
Day 4:
9,999 billion or rather 10 billion years after the Big Bang
God said, let the waters under the heaven
be gathered together unto one place and let the dry land appear.
“Earth” was “liquid”
with a heavy “mineral” content. The liquid and minerals divided, and land appeared. God called the dry substance
land or earth, and the gathering of the waters he called sea.
Once divided, rain or fog could start,
because the earth is warm and water cold as a result winds started and brought forth rain, which was necessary for the development
of plants. See Gen.2: 4-6.
Gen. 1 verse 11: and God said, let
the earth bring forth grass, herb yielding seed and the fruit tree yielding fruit after his kind, whose seed is in itself
upon the earth
To prepare for humans and animals, the
earth started provision of oxygen.
Evolution/development/creation/ was in
this sequence:
Grass evolved into herb yielding seed,
which evolved into fruit bearing trees, with fruit whose seed is within itself (discussed in detail in this manuscript.)
The Hebrew meaning for the word grass
describes something similar to algae, which developed into herb and later into distinct species of trees etc. (to its kind)
Logically sea or water plants also started
like algae.
We’re all used to the term senses.
Grass (Heb)
deshe’ = tender) has 1 sense. Herb 2 senses. Fruit trees 3 senses, fish 4 senses,
animals 5 senses, human 6 senses.
Senses in fact = spirit = God.
Plants have a breathing/respiration system.
It uses air, therefore this is the first kind of spirit exchange (God is spirit) and there is no “movement” or
creatures yet.
Day 5: Verse 20: God said, let the waters
bring forth abundantly, the moving creatures that has life, and fowl that may fly above the earth in the open
firmament of heaven.
Moving creatures: a swarm of minute animals,
creeping or moving things (organisms).
Life: to come alive (however they are
not breathing creatures yet.)
Now for the first time life with “real”
spirit and movement roams the land.
Verse 21: God created great whales and
living creatures, which the water brought forth abundantly, after their kind and every winged fowl after his
kind (the word “his” is used because it refers to male)
Whales: monsters.
Living creatures: breathing creatures/animals
with a mental mind. (They started to develop a mind and lungs).
The first creatures were moving creatures
with life, which have now evolved into living creatures that have breath.
Day 6:
Verse 24: God said, let the earth bring forth living creatures (on day 5 the water brought forth creatures) of its
kind, cattle, and creeping things, and beasts of the earth after its kind.
It happened in this order:
Living creatures with low mind function,
came out of the water onto the land and systematically “evolved” into cattle. They were obviously breathing creatures
as the meaning describes.
Cattle: a water ox/ hippopotamus or Nile
horse
Further meaning: to be mute, (a dumb beast
without sound (voice) or hearing.)
Hearing and sound was created on earth
not in water.
Beast: running creatures.
All these animals and later on the”
human”, described in Gen 4:17-23 were hermaphrodites, they impregnated themselves so to speak, this is discussed and
proved in another chapter.
Then 555,555 million years ago God said:
verse 26; let us make man in our image, after our likeness. Someone said to me; “God was lonely” and wanted to
create children; yes it is true but who is us and our in verse 26 then, because it suggests that God was after all not alone?
We discuss who this “us” and
“our” exactly is in another chapter.
Image: to shade, a phantom, an illusion,
resemblance representative figure or an idol.
Likeness: resemblance, model, shape, advance
like fashion, manner, to resemble, consider, and comparison device, think, similitude.
Verse 27: so God created man in his own
image, in the image of God created he him.
Then God says exactly what he means by
his image: he says, male and female He created them.
In fact, what God is saying is: his image
is male and female in one body. We are created to this same image and likeness.
I want to make this very clear; God says;
he = male and female.
So the conclusion is that you and me are
male and female in the same/one body!!!
Remember, the scripture says husband and
wife will become one flesh. How you might ask? Only in their offspring is it possible! When a child is created, the
child inherits its genes from his parents; 50% from the father, and 50% from the mother. Therefore, only by way of their
children, man and wife can become one flesh; there is no other way.
This matter is discussed further in another
chapter of this manuscript, for it holds huge mystery and revelations.
Out of all this we can clearly establish
that humans were created/evolved from animals.
Does that change your purpose, your dignity,
and your pride? For God said He will create children out of rock. Humans were created on the sixth day and will disappear
the same day…
The glorified humans were created to ultimately,
on the seventh day, rule the universe. Therefore it only makes sense that humans evolved from rock to grass to fish to land
animal to human. A glorified body is surely a better form of advance/evolution of the mortal body we now know to the ultimate
future glorified body.
Humans were therefore created out of all
the substances of the universe. It cannot be otherwise because if we need the knowledge to rule the universe there is no better
way as to have the contents of the universe.
Heaven and earth impregnated each other
by way of the Big Bang, where the “atoms” of heaven and the “atoms” of earth melted together in the
womb of earth.
In their children, you and me the universe
became one flesh!
I say; Heaven and earth became one
flesh in you and me, because we have the same genes as our parents.
SUMMARY.
You can now clearly understand that the
bible describes creation “exactly” the way scientists describes it, for it clearly describes the Big Bang and
the way everything were created; in fact it describes it better than the scientists and they can now learn from the bible.
The word evolve which scientists
use has the same meaning as to its kind, the word the bible use to describe the creation of life.
The universe itself has evolved from the
Big Bang, which started with a vacuum to what we have today.
The following can bee seen on a web site;
www.exploratorium.edu/origins/cern/ideas/bang.
Quote; The universe began, scientists
believe, with every speck of its energy jammed into a very tiny point. This extremely dense point exploded with unimaginable
force, creating matter and propelling it outward to make the billions of galaxies of our vast universe. Astrophysicists dubbed
this titanic explosion the Big Bang.
For a brief
moment after the Big Bang, the immense heat created conditions unlike any conditions astrophysicists see in the universe today.
While planets and stars today are composed of atoms of elements like hydrogen and silicon, scientists believe the universe
back then was too hot for anything other than the most fundamental particles -- such as quarks and photons.
But as
the universe quickly expanded, the energy of the Big Bang became more and more "diluted" in space, causing the universe to
cool. Popping open a beer bottle results in a roughly similar cooling, expanding effect: gas, once confined in the bottle,
spreads into the air, and the temperature of the beer drops.
Rapid cooling allowed for matter as we know it to form
in the universe, although physicists are still trying to figure out exactly how this happened. About one ten-thousandth of
a second after the Big Bang, protons and neutrons formed, and within a few minutes these particles stuck together to form
atomic nuclei, mostly hydrogen and helium. Hundreds of thousands of years later, electrons stuck to the nuclei to make complete
atoms.
About a billion years after the Big Bang, gravity caused these atoms to gather in huge clouds of gas, forming
collections of stars known as galaxies. Gravity is the force that pulls any objects with mass towards one another -- the same
force, for example, that causes a ball thrown in the air to fall to the earth.
Where do planets
like earth come from? Over billions of years, stars "cook" hydrogen and helium atoms in their hot cores to make heavier elements
like carbon and oxygen. Large stars explode over time, blasting these elements into space. This matter then condenses into
the stars, planets, and satellites that make up solar systems like our own.
End of quote.
Therefore;
we can understand that the universe went through a process of “evolution”, which produced different materials
from the combination of different atoms.
Did you know
that the matter of your body are millions of years old?
Out of these discussions we can clearly
understand that earth acts as the womb of creation because she is the one to bear children like plants and animals and
humans.
Heaven would therefore act as the male
to impregnate earth with different sperm cells. We discuss this later on in this revelation.
You can now look at the pictures below
and decide for yourself; 1) was there a Big Bang; 2) has God already finished the universe as believed by some that the universe
were created in 144 hours; 3) is God/the universe still busy creating/recreating itself to better itself; 4) does there also
wait for us a sudden transformation/metamorphoses in future?
One
of the biggest mysteries in cosmology could be explained by a controversial theory in which the universe explodes into existence
not just once, but repeatedly in endless cycles of death and rebirth.

Quantum
physics tells us that contrary to appearances, empty space is a bubbling brew of "virtual" subatomic particles that are constantly
being created and destroyed. The fleeting particles endow every cubic centimeter of space with a certain energy that, according to general relativity, produces an anti-gravitational force that pushes space apart. Nobody knows what's
really causing the accelerated expansion of the universe, however.
Credit:
NASA-JSC-ES&IA

BLACK HOLE
When a supermassive
star dies, its corpse collapses into a knot so tight not even light can escape. And this drain on the fabric of the Universe
can actually warp the shape of space... and of time.
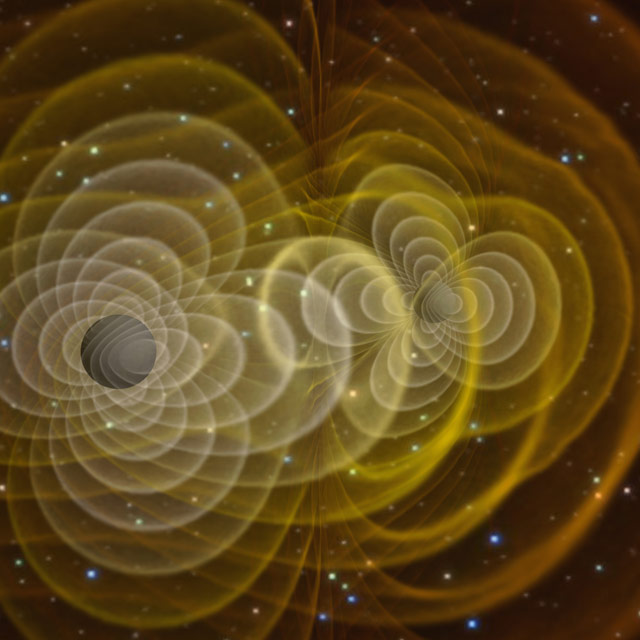
Gravity
Waves
Gravity
waves are distortions in the fabric of space-time predicted by Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. The waves travel at the speed of
light, but they are so weak that scientists expect to detect only those created during colossal cosmic events, such as black hole mergers like the one shown above. LIGO and LISA are two detectors designed to spot the elusive waves.
|
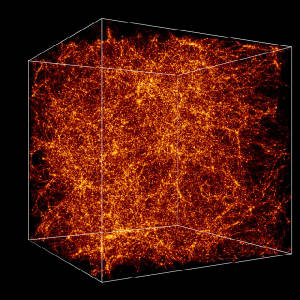
Dark
Matter
Scientists
think it makes up the bulk of matter in the universe, but it can neither be seen nor detected directly using current technologies.
Candidates range from light-weight neutrinos to invisible black holes. Some scientists question whether dark matter is even real, and suggest that the mysteries it was conjured to solve could be explained by a better understanding of gravity.
Credit:
Andrey Kravtsov |

Like life on Earth, galaxies can "eat" each other and evolve over time. The Milky Way's neighbor, Andromeda, is currently dining on one of its satellites. More than a dozen star clusters are scattered throughout Andromeda, the cosmic remains of past meals. The image above is from a simulation of Andromeda and our galaxy colliding, an event that will take place in about 3 billion years.

|
Mini-Black
Holes
If
a radical new "braneworld" theory of gravity is correct, then scattered throughout our solar system are thousands of tiny black holes, each about the size of an atomic nucleus. Unlike their larger brethren, these mini-black holes are primordial leftovers from the Big Bang and affect space-time differently because of their close association with a fifth dimension.
Credit:
NASA-MSFC |

Cosmic
Microwave Background
Also
known as the CMB, this radiation is a primordial leftover from the Big Bang that birthed the universe. It was first detected during the 1960s
as a radio noise that seemed to emanate from everywhere in space. The CMB is regarded as one of the best pieces of evidence
for the theoretical Big Bang. Recent precise measurements by the WMAP project place the CMB temperature at -455 degrees Fahrenheit (-270 Celsius). Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team
Here is a scientific explanation
of how the earth evolved and came into being.
History
of Earth
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to:
navigation, search
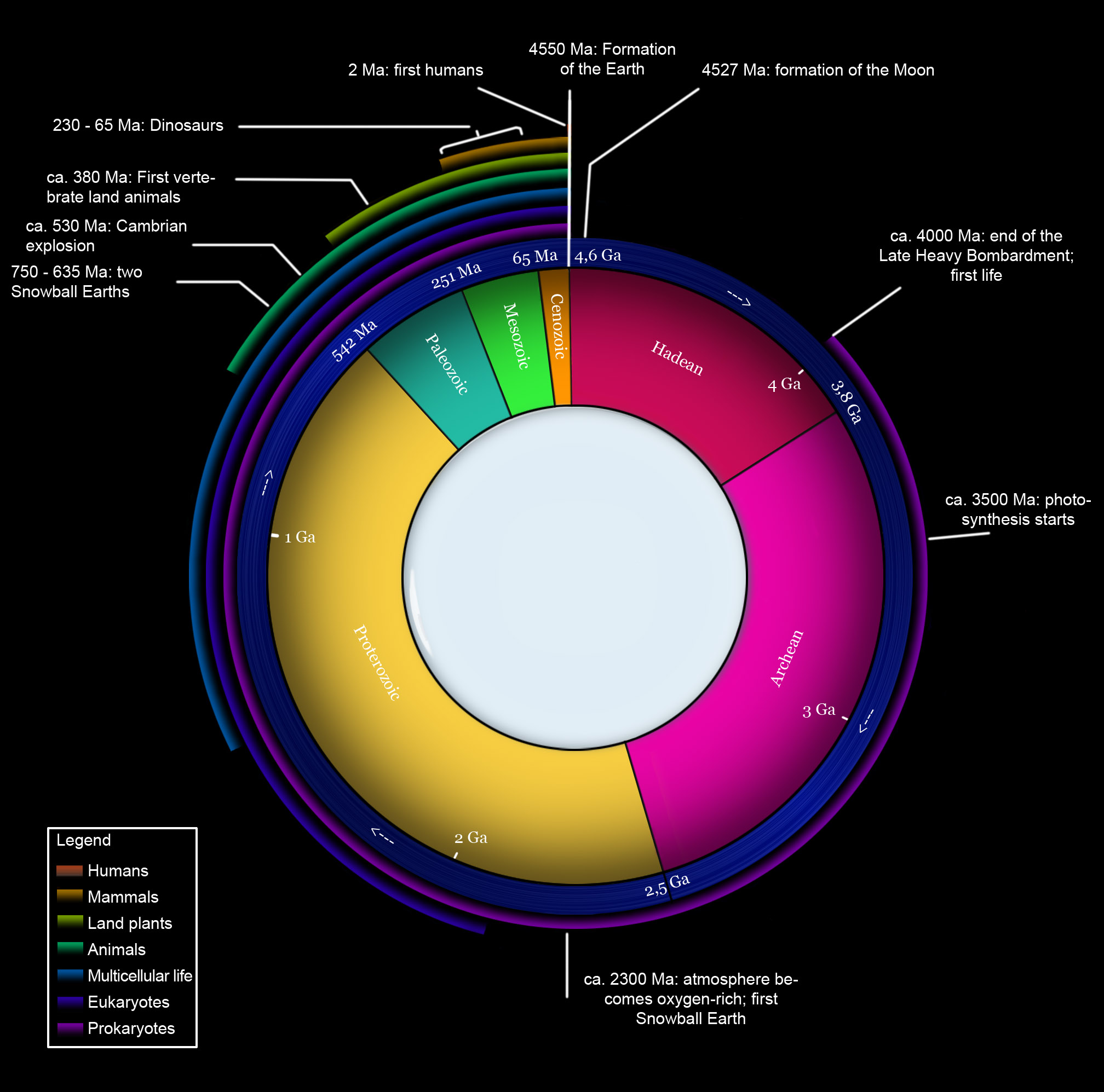
Geological
time put in a diagram called a geological clock, showing the relative lengths of the eons of the Earth's history.
For the
history of modern humans, see History of the world.
The history
of Earth covers approximately 4.6 billion years (4,567,000,000 years), from Earth’s formation out of the solar nebula to the present. This article presents a broad overview, summarizing the leading, most current scientific theories.
Origin

An artist's
impression of protoplanetary disk.
Main article: Formation and evolution of the Solar System
The Earth
formed as part of the birth of the Solar System: what eventually became the solar system initially existed as a large, rotating cloud of dust, rocks, and gas. It was composed of hydrogen and helium produced in the Big Bang, as well as heavier elements ejected by supernovas. Then, as one theory suggests, about 4.6 billion years ago a nearby star was destroyed in a supernova and the explosion sent a shock wave through the solar nebula, causing it to gain angular momentum. As the cloud began to accelerate its rotation, gravity and inertia flattened it into a protoplanetary disk oriented perpendicularly to its axis of rotation. Most of the mass concentrated in the middle and began to heat up, but small
perturbations due to collisions and the angular momentum of other large debris created the means by which protoplanets began to form. The infall of material, increase in rotational speed and the crush of gravity created an enormous amount of
kinetic heat at the center. Its inability to transfer that energy away through any other process at a rate capable of relieving the build-up
resulted in the disk's center heating up. Ultimately, nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium began, and eventually, after contraction, a T Tauri star, ignited to create the Sun. Meanwhile, as gravity caused matter to condense around the previously perturbed objects outside of the new sun's gravity grasp, dust particles and the rest of
the protoplanetary disk began separating into rings. Successively larger fragments collided with one another and became larger objects, ultimately
destined to become protoplanets.[1] These included one collection approximately 150 million kilometers from the center: Earth. The solar wind of the newly formed T Tauri star cleared out most of the material in the disk that had not already condensed into larger
bodies.
Moon
An artist's
impression of protoplanetary disk.
Main article: Formation and evolution of the Solar System
The Earth
formed as part of the birth of the Solar System: what eventually became the solar system initially existed as a large, rotating cloud of dust, rocks, and gas. It was composed of hydrogen and helium produced in the Big Bang, as well as heavier elements ejected by supernovas. Then, as one theory suggests, about 4.6 billion years ago a nearby star was destroyed in a supernova and the explosion sent a shock wave through the solar nebula, causing it to gain angular momentum. As the cloud began to accelerate its rotation, gravity and inertia flattened it into a protoplanetary disk oriented perpendicularly to its axis of rotation. Most of the mass concentrated in the middle and began to heat up, but small
perturbations due to collisions and the angular momentum of other large debris created the means by which protoplanets began to form. The infall of material, increase in rotational speed and the crush of gravity created an enormous amount of
kinetic heat at the center. Its inability to transfer that energy away through any other process at a rate capable of relieving the build-up
resulted in the disk's center heating up. Ultimately, nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium began, and eventually, after contraction, a T Tauri star, ignited to create the Sun. Meanwhile, as gravity caused matter to condense around the previously perturbed objects outside of the new sun's gravity grasp, dust particles and the rest of
the protoplanetary disk began separating into rings. Successively larger fragments collided with one another and became larger objects, ultimately
destined to become protoplanets.[1] These included one collection approximately 150 million kilometers from the center: Earth. The solar wind of the newly formed T Tauri star cleared out most of the material in the disk that had not already condensed into larger
bodies.
Moon
Animation
(not to scale) of Theia forming in Earth’s L5 point and then, perturbed by gravity, colliding to help form the moon. The animation progresses in one-year steps making Earth
appear not to move. The view is of the south pole.
Main articles: Moon#Origin and geologic evolution and Giant impact hypothesis
The origin
of the Moon is still uncertain, although much evidence exists for the giant impact hypothesis. Earth may not have been the only planet
forming 150 million kilometers from the Sun. It is hypothesized that another collection occurred 150 million kilometers from
both the Sun and the Earth, at their fourth or fifth Lagrangian point. This planet, named Theia, is thought to have been smaller than the current Earth, probably about the size and mass of Mars. Its orbit may at first have been stable, but destabilized as Earth increased its mass by the accretion of more and more
material. Theia swung back and forth relative to Earth until, finally, an estimated 4.533 billion years ago,[2] it collided at a low, oblique angle. The low speed and angle were not enough to destroy Earth, but a large portion
of its crust was ejected into space. Heavier elements from Theia sank to Earth’s core, while the remaining material
and ejecta condensed into a single body within a couple of weeks. Under the influence of its own gravity, this became a more
spherical body: the Moon.[3] The impact is also thought to have changed Earth’s axis to produce the large 23.5° axial tilt that is responsible for Earth’s seasons. (A simple, ideal model of the planets’ origins would have axial tilts
of 0° with no recognizable seasons.) It may also have sped up Earth’s rotation and initiated the planet’s plate tectonics.
The Hadean eon
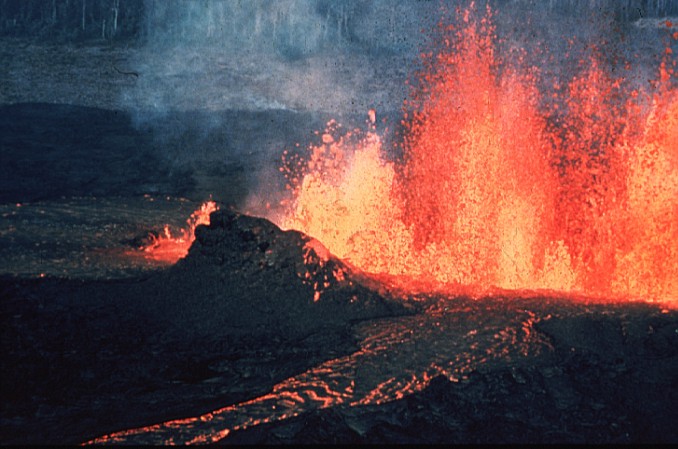

Volcanic
eruptions would have been common in Earth's early days.
The early
Earth, during the very early Hadean eon, was very different from the world known today. There were no oceans and no oxygen in the atmosphere. It was bombarded
by planetoids and other material left over from the formation of the solar system. This bombardment, combined with heat from
radioactive breakdown, residual heat, and heat from the pressure of contraction, caused the planet at this stage to be fully
molten. During the iron catastrophe heavier elements sank to the center while lighter ones rose to the surface producing the layered structure of the Earth and also setting up the formation of Earth's magnetic field. Earth's early atmosphere would have comprised surrounding material from the solar nebula, especially light gases such as
hydrogen and helium, but the solar wind and Earth's own heat would have driven off this atmosphere.
This changed
when Earth was about 40% its present radius, and gravitational attraction allowed the retention of an atmosphere which included
water. Temperatures plummeted and the crust of the planet was accumulated on a solid surface, with areas melted by large impacts
on the scale of decades to hundreds of years between impact. Large impacts would have caused localized melting and partial
differentiation, with some lighter elements on the surface or released to the moist atmosphere. [4]
The surface
cooled quickly, forming the solid crust within 150 million years;[5] although new research[6] suggests that the actual number is 100 million years based on the level of hafnium found in the geology at Jack hills in Western Australia. From 4 to 3.8 billion years ago, Earth underwent a period of heavy asteroidal bombardment.[7] Steam escaped from the crust while more gases were released by volcanoes, completing the second atmosphere. Additional water was imported by bolide collisions, probably from asteroids ejected from the outer asteroid belt under the influence of Jupiter's gravity. The planet
cooled. Clouds formed. Rain gave rise to the oceans within 750 million years (3.8 billion years ago), but probably earlier. Recent evidence suggests the oceans may have begun forming by 4.2 billion years ago[8] [9]. The new atmosphere probably contained ammonia, methane, water vapor, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen, as well as smaller amounts of other gases. Any free oxygen would have been bound by hydrogen or minerals on the surface.
Volcanic activity was intense and, without an ozone layer to hinder its entry, ultraviolet radiation flooded the surface.
Life
The replicator
in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate.
Main article:
Origin of life
The details
of the origin of life are unknown, though the broad principles have been established. Two schools of thought regarding the
origin of life have been proposed. The first suggest that organic components may have arrived on Earth from space (see “Panspermia”), while the other argues for terrestrial origins. The mechanisms by which life would initially arise are nevertheless
held to be similar.[10] If life arose on Earth, the timing of this event is highly speculative—perhaps it arose around 4 billion years
ago.[11] In the energetic chemistry of early Earth, a molecule (or even something else) gained the ability to make copies of
itself–the replicator. The nature of this molecule is unknown, its function having long since been superseded by life’s
current replicator, DNA. In making copies of itself, the replicator did not always perform accurately: some copies contained an “error.”
If the change destroyed the copying ability of the molecule, there could be no more copies, and the line would “die
out.” On the other hand, a few rare changes might make the molecule replicate faster or better: those “strains”
would become more numerous and “successful.” As choice raw materials (“food”) became depleted, strains
which could exploit different materials, or perhaps halt the progress of other strains and steal their resources, became more
numerous.[12]
Several
different models have been proposed explaining how a replicator might have developed. Different replicators have been posited,
including organic chemicals such as modern proteins, nucleic acids, phospholipids, crystals,[13] or even quantum systems.[14] There is currently no method of determining which of these models, if any, closely fits the origin of life on Earth. One of the older theories, and one which has been worked out in some detail, will serve as an example of how this might
occur. The high energy from volcanoes, lightning, and ultraviolet radiation could help drive chemical reactions producing more complex molecules from simple compounds such as methane and ammonia.[15] Among these were many of the relatively simple organic compounds that are the building blocks of life. As the amount of this “organic soup” increased, different molecules
reacted with one another. Sometimes more complex molecules would result—perhaps clay provided a framework to collect and concentrate organic material.[16] The presence of certain molecules could speed up a chemical reaction. All this continued for a very long time, with reactions occurring more or less at random, until by chance
there arose a new molecule: the replicator. This had the bizarre property of promoting the chemical reactions which produced a copy of itself, and evolution began properly. Other theories posit a different replicator. In any case, DNA took over the function of the replicator at
some point; all known life (with the exception of some viruses and prions) use DNA as their replicator, in an almost identical manner (see genetic code).
Cells
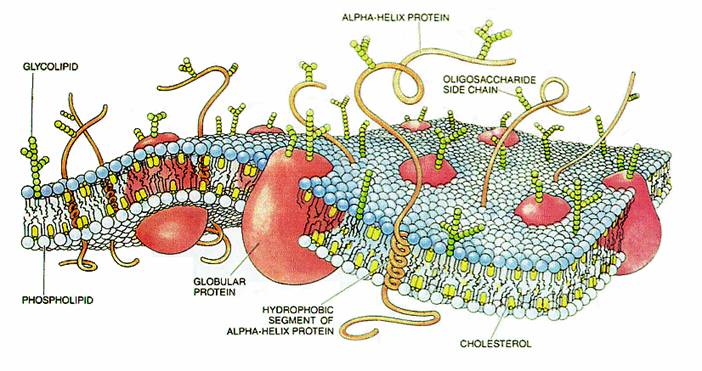
A small
section of a cell membrane. This modern cell membrane is far more sophisticated than the original simple phospholipid bilayer
(the small blue spheres with two tails). Proteins and carbohydrates serve various functions in regulating the passage of material through the membrane and in reacting to the environment.
Modern
life has its replicating material packaged neatly inside a cellular membrane. It is easier to understand the origin of the cell membrane than the origin of the replicator, since the phospholipid molecules that make up a cell membrane will often form a bilayer spontaneously when placed in water. Under certain conditions, many such spheres can be formed (see “The bubble theory”).[17] It is not known whether this process preceded or succeeded the origin of the replicator (or perhaps it was the replicator).
The prevailing theory is that the replicator, perhaps RNA by this point (the RNA world hypothesis), along with its replicating apparatus and maybe other biomolecules, had already evolved. Initial protocells may have simply burst when they grew too large; the scattered contents may then have recolonized other “bubbles.”
Proteins that stabilized the membrane, or that later assisted in an orderly division, would have promoted the proliferation of those
cell lines. RNA is a likely candidate for an early replicator since it can both store genetic information and catalyze reactions. At some point DNA took over the genetic storage role from RNA, and proteins known as enzymes took over the catalysis role, leaving RNA to transfer information and modulate the process. There is increasing belief that
these early cells may have evolved in association with underwater volcanic vents known as “black smokers”.[18] or even hot, deep rocks.[19] However, it is believed that out of this multiplicity of cells, or protocells, only one survived. Current evidence
suggests that the last universal common ancestor lived during the early Archean eon, perhaps roughly 3.5 billion years ago or earlier.[20],[21] This “LUCA” cell is the ancestor of all cells and hence all life on Earth. It was probably a prokaryote, possessing a cell membrane and probably ribosomes, but lacking a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. Like all modern cells, it used DNA as its genetic code, RNA for information transfer and protein synthesis, and enzymes to catalyze reactions. Some scientists believe that instead of a single organism being the last universal common ancestor,
there were populations of organisms exchanging genes in lateral gene transfer.[20]
Photosynthesis and oxygen
The harnessing
of the sun’s energy led to several major changes in life on Earth.
It is likely
that the initial cells were all heterotrophs, using surrounding organic molecules (including those from other cells) as raw material and an energy source.[22] As the food supply diminished, a new strategy evolved in some cells. Instead of relying on the diminishing amounts
of free-existing organic molecules, these cells adopted sunlight as an energy source. Estimates vary, but by about 3 billion years ago[23], something similar to modern photosynthesis had probably developed. This made the sun’s energy available not only to autotrophs but also to the heterotrophs that consumed them. Photosynthesis used the plentiful carbon dioxide and water as raw materials and, with the energy of sunlight, produced energy-rich organic molecules (carbohydrates).
Moreover,
oxygen was produced as a waste product of photosynthesis. At first it became bound up with limestone, iron, and other minerals. There is substantial proof of this in iron-oxide rich layers in geological strata that correspond with
this time period. The oceans would have turned to a green color while oxygen was reacting with minerals. When the reactions
stopped, oxygen could finally enter the atmosphere. Though each cell only produced a minute amount of oxygen, the combined
metabolism of many cells over a vast period of time transformed Earth’s atmosphere to its current state.[24]
This, then,
is Earth’s third atmosphere. Some of the oxygen was stimulated by incoming ultraviolet radiation to form ozone, which collected in a layer near the upper part of the atmosphere. The ozone layer absorbed, and still absorbs, a significant
amount of the ultraviolet radiation that once had passed through the atmosphere. It allowed cells to colonize the surface
of the ocean and ultimately the land:[25] without the ozone layer, ultraviolet radiation bombarding the surface would have caused unsustainable levels of mutation in exposed cells. Besides making large amounts of energy available to life-forms and blocking ultraviolet radiation, the
effects of photosynthesis had a third, major, and world-changing impact. Oxygen was toxic; probably much life on Earth died
out as its levels rose (the “Oxygen Catastrophe”).[25] Resistant forms survived and thrived, and some developed the ability to use oxygen to enhance their metabolism and
derive more energy from the same food.
Endosymbiosis and the three domains of life
Main article:
Endosymbiotic theory
Some of
the pathways by which the various endosymbionts might have arisen.
Modern
taxonomy classifies life into three domains. The time of the origin of these domains are speculative. The Bacteria domain probably first split off from the other forms of life (sometimes called Neomura), but this supposition is controversial. Soon after this, by 2 billion years ago[26], the Neomura split into the Archaea and the Eukarya. Eukaryotic cells (Eukarya) are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells (Bacteria and Archaea), and the origin of
that complexity is only now coming to light. Around this time period a bacterial cell related to today’s Rickettsia[27] entered a larger prokaryotic cell. Perhaps the large cell attempted to ingest the smaller one but failed (maybe due
to the evolution of prey defenses). Perhaps the smaller cell attempted to parasitize the larger one. In any case, the smaller
cell survived inside the larger cell. Using oxygen, it was able to metabolize the larger cell’s waste products and derive more energy. Some of this surplus energy was
returned to the host. The smaller cell replicated inside the larger one, and soon a stable symbiotic relationship developed. Over time the host cell acquired some of the genes of the smaller cells, and the two kinds became
dependent on each other: the larger cell could not survive without the energy produced by the smaller ones, and these in turn
could not survive without the raw materials provided by the larger cell. Symbiosis developed between the larger cell and the population of smaller cells inside it to the extent that they are considered to
have become a single organism, the smaller cells being classified as organelles called mitochondria. A similar event took place with photosynthetic cyanobacteria[28] entering larger heterotrophic cells and becoming chloroplasts.[29],[30] Probably as a result of these changes, a line of cells capable of photosynthesis split off from the other eukaryotes
some time before one billion years ago. There were probably several such inclusion events, as the figure at right suggests.
Besides the well-established endosymbiotic theory of the cellular origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts, it has been suggested
that cells gave rise to peroxisomes, spirochetes gave rise to cilia and flagella, and that perhaps a DNA virus gave rise to the cell nucleus,[31],[32] though none of these theories are generally accepted.[33] During this period, the supercontinent Columbia is believed to have existed, probably from around 1.8 to 1.5 billion years ago; it is the oldest hypothesized supercontinent.[34]
Multicellularity
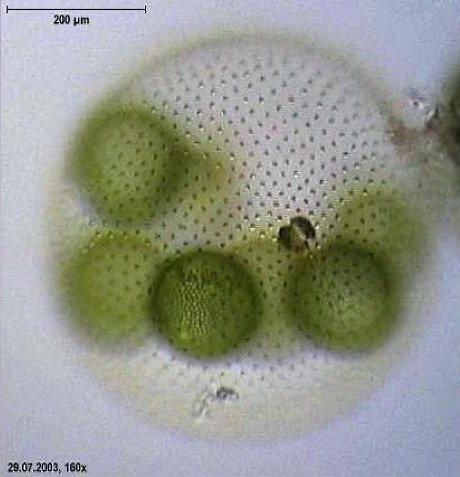
Volvox aureus is believed to be similar to the first multicellular plants.
Archaeans,
bacteria, and eukaryotes continued to diversify and to become more sophisticated and better adapted to their environments.
Each domain repeatedly split into multiple lineages, although little is known about the history of the archaea and bacteria.
Around 1.1 billion years ago, the supercontinent Rodinia was assembling.[35] The plant, animal, and fungi lines had all split, though they still existed as solitary cells. Some of these lived in colonies, and gradually some division of labor began to take place; for instance, cells on the periphery might have started to assume different roles from those in the
interior. Although the division between a colony with specialized cells and a multicellular organism is not always clear,
around 1 billion years ago[36], the first multicellular plants emerged, probably green algae.[37] Possibly by around 900 million years ago,[38] true multicellularity had also evolved in animals. At first it probably somewhat resembled that of today’s sponges, where all cells were totipotent and a disrupted organism could reassemble itself.[39] As the division of labor became more complete in all lines of multicellular organisms, cells became more specialized
and more dependent on each other; isolated cells would die. Many scientists believe that a very severe ice age began around
770 million years ago, so severe that the surface of all the oceans completely froze (Snowball Earth). Eventually, after 20 million years, enough carbon dioxide escaped through volcanic outgassing; the resulting greenhouse
effect raised global temperatures.[40] By around the same time, 750 million years ago,[41] Rodinia began to break up.
Colonization of land
For most
of Earth’s history, there were no multicellular organisms on land. Parts of the surface may have vaguely resembled this
view of Mars, one of Earth’s neighboring planets.[citation needed]
As we have
already seen, the accumulation of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere caused the formation of ozone into a layer that absorbed much of Sun’s ultraviolet radiation. As a result, unicellular organisms that reached land were less likely to die, and prokaryotes began to multiply and become
better adapted to survival out of the water. Prokaryotes had likely colonized the land as early as 2.6 billion years ago[42] even before the origin of the eukaryotes. For a long time, the land remained barren of multicellular organisms. The
supercontinent Pannotia formed around 600 million years ago and then broke apart a short 50 million years later[43]. Fish, the earliest vertebrates, evolved in the oceans around 530 million years ago[44]. A major extinction event occurred near the end of the Cambrian period,[45] which ended 488 million years ago[46].
Several
hundred million years ago, plants (probably resembling algae) and fungi started growing at the edges of the water, and then out of it.[47] The oldest fossils of land fungi and plants date to 480–460 million years ago, though molecular evidence suggests
the fungi may have colonized the land as early as 1000 million years ago and the plants 700 million years ago.[48] Initially remaining close to the water’s edge, mutations and variations resulted in further colonization of this
new environment. The timing of the first animals to leave the oceans is not precisely known: the oldest clear evidence is
of arthropods on land around 450 million years ago[49], perhaps thriving and becoming better adapted due to the vast food source provided by the terrestrial plants. There
is also some unconfirmed evidence that arthropods may have appeared on land as early as 530 million years ago[50]. At the end of the Ordovician period, 440 million years ago, additional extinction events occurred, perhaps due to a concurrent ice age.[51] Around 380 to 375 million years ago, the first tetrapods evolved from fish.[52] It is thought that perhaps fins evolved to become limbs which allowed the first tetrapods to lift their heads out of
the water to breathe air. This would let them survive in oxygen-poor water or pursue small prey in shallow water.[52] They may have later ventured on land for brief periods. Eventually, some of them became so well adapted to terrestrial
life that they spent their adult lives on land, although they hatched in the water and returned to lay their eggs. This was
the origin of the amphibians. About 365 million years ago, another period of extinction occurred, perhaps as a result of global cooling.[53] Plants evolved seeds, which dramatically accelerated their spread on land, around this time (by approximately 360 million years ago).[54], [55]
Pangaea, the most recent supercontinent, existed from 300 to 180 million years ago. The outlines of the modern continents and other
land masses are indicated on this map.
Some 20
million years later (340 million years ago[56]), the amniotic egg evolved, which could be laid on land, giving a survival advantage to tetrapod embryos. This resulted in the divergence of amniotes from amphibians. Another 30 million years (310 million years ago[57]) saw the divergence of the synapsids (including mammals) from the sauropsids (including birds and non-avian, non-mammalian reptiles). Other groups of organisms continued to evolve and lines diverged—in fish, insects, bacteria, and so on—but
less is known of the details. 300 million years ago, the most recent hypothesized supercontinent formed, called Pangaea. The most severe extinction event to date took place 250 million years ago, at the boundary of the Permian and Triassic periods; 95% of life on Earth died out,[58] possibly due to the Siberian Traps volcanic event. The discovery of the Wilkes Land crater in Antarctica may suggest a connection with the Permian-Triassic extinction, but the age of that crater is not known.[59] But life persevered, and around 230 million years ago [60], dinosaurs split off from their reptilian ancestors. An extinction event between the Triassic and Jurassic periods 200 million years ago spared many of the dinosaurs,[61] and they soon became dominant among the vertebrates. Though some of the mammalian lines began to separate during this
period, existing mammals were probably all small animals resembling shrews.[62] By 180 million years ago, Pangaea broke up into Laurasia and Gondwana. The boundary between avian and non-avian dinosaurs is not clear, but Archaeopteryx, traditionally considered one of the first birds, lived around 150 million years ago.[63] The earliest evidence for the angiosperms evolving flowers is during the Cretaceous period, some 20 million years later (132 million years ago)[64] Competition with birds drove many pterosaurs to extinction, and the dinosaurs were probably already in decline for various reasons[65] when, 65 million years ago, a 10-kilometer meteorite likely struck Earth just off the Yucatán Peninsula, ejecting vast quantities of particulate matter and vapor into the air that occluded sunlight, inhibiting photosynthesis.
Most large animals, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct.[66], marking the end of the Cretaceous period and Mesozoic era. Thereafter, in the Paleocene epoch, mammals rapidly diversified, grew larger, and became the dominant vertebrates. Perhaps a couple of million years later
(around 63 million years ago), the last common ancestor of primates lived.[67] By the late Eocene epoch, 34 million years ago, some terrestrial mammals had returned to the oceans to become animals such as Basilosaurus which later gave rise to dolphins and whales.[68]
Humanity

Australopithecus africanus, an early hominid.
Main article: Human evolution
A small
African ape living around six million years ago was the last animal whose descendants would include both modern humans and
their closest relatives, the bonobos, and chimpanzees.[69] Only two branches of its family tree have surviving descendants. Very soon after the split, for reasons that are still
debated, apes in one branch developed the ability to walk upright.[70] Brain size increased rapidly, and by 2 million years ago, the very first animals classified in the genus Homo had appeared.[71] Of course, the line between different species or even genera is rather arbitrary as organisms continuously change over
generations. Around the same time, the other branch split into the ancestors of the common chimpanzee and the ancestors of the bonobo as evolution continued simultaneously in all life forms.[69] The ability to control fire likely began in Homo erectus (or Homo ergaster), probably at least 790,000 years ago[72] but perhaps as early as 1.5 million years ago.[73] It is more difficult to establish the origin of language; it is unclear whether Homo erectus could speak or if that capability had not begun until Homo sapiens.[74] As brain size increased, babies were born sooner, before their heads grew too large to pass through the pelvis. As a result, they exhibited more plasticity, and thus possessed an increased capacity to learn and required a longer period of dependence. Social skills became more
complex, language became more advanced, and tools became more elaborate. This contributed to further cooperation and brain
development.[75] Anatomically modern humans — Homo sapiens — are believed to have originated somewhere around 200,000 years ago or earlier in Africa; the oldest fossils date back to around 160,000 years ago.[76] The first humans to show evidence of spirituality are the Neanderthals (usually classified as a separate species with no surviving descendants); they buried their dead, often apparently with food
or tools.[77] However, evidence of more sophisticated beliefs, such as the early Cro-Magnon cave paintings (probably with magical or religious significance)[78] did not appear until some 32,000 years ago.[79] Cro-Magnons also left behind stone figurines such as Venus of Willendorf, probably also signifying religious belief.[78] By 11,000 years ago, Homo sapiens had reached the southern tip of South America, the last of the uninhabited continents.[80] Tool use and language continued to improve; interpersonal relationships became more complex.
Civilization
Main article: History of the world
Throughout
more than 90% of its history, Homo sapiens lived in small bands as nomadic hunter-gatherers.[81] As language became more complex, the ability to remember and transmit information resulted in a new sort of replicator:
the meme.[82] Ideas could be rapidly exchanged and passed down the generations. Cultural evolution quickly outpaced biological evolution, and history proper began. Somewhere between 8500 and 7000 BC, humans in the Fertile Crescent in Middle East began the systematic husbandry of plants and animals: agriculture.[83] This spread to neighboring regions, and also developed independently elsewhere, until most Homo sapiens lived sedentary
lives in permanent settlements as farmers. Not all societies abandoned nomadism, especially those in isolated areas of the
globe poor in domesticable plant species, such as Australia.[84] However, among those civilizations that did adopt agriculture, the relative security and increased productivity provided
by farming allowed the population to expand. Agriculture had a major impact; humans began to affect the environment as never
before. Surplus food allowed a priestly or governing class to arise, followed by increasing division of labor. This led to Earth’s first civilization at Sumer in the Middle East, between 4000 and 3000 BC.[85] Additional civilizations quickly arose in ancient Egypt and the Indus River valley.
Starting
around 3000 BC, Hinduism, one of the oldest religions still practiced today, began to take form.[86] Others soon followed. The invention of writing enabled complex societies to arise: record-keeping and libraries served as a storehouse of knowledge and increased the cultural transmission of information. Humans no longer had to spend
all their time working for survival—curiosity and education drove the pursuit of knowledge and wisdom. Various disciplines,
including science (in a primitive form), arose. New civilizations sprang up, traded with one another, and engaged in war for territory and resources: empires began to form. By around 500 BC, there were empires in the Middle East, Iran, India, China, and Greece, approximately on
equal footing; at times one empire expanded, only to decline or be driven back later.[87]
In the
fourteenth century, the Renaissance began in Italy with advances in religion, art, and science.[88] Starting around 1500, European civilization began to undergo changes leading to the scientific and industrial revolutions: that continent began to exert political and cultural dominance over human societies around the planet.[89] From 1914 to 1918 and 1939 to 1945, nations around the world were embroiled in world wars. Established following World War I, the League of Nations was a first step toward a world government; after World War II it was replaced by the United Nations. In 1992, several European nations joined together in the European Union. As transportation and communication improved, the economies and political affairs of nations around the world have become
increasingly intertwined. This globalization has often produced discord, although increased collaboration has resulted as well.
Recent events
Four and
a half billion years after the planet's formation, one of Earth’s life forms broke free of the biosphere. For the first time in history, Earth was viewed first hand from the vantage of space.
Change
has continued at a rapid pace from the mid-1940s to today. Technological developments include nuclear weapons, computers, genetic engineering, and nanotechnology. Economic globalization spurred by advances in communication and transportation technology has influenced everyday life in many parts of the world.
Cultural and institutional forms such as democracy, capitalism, and environmentalism have increased influence. Major concerns and problems such as disease, war, poverty, violent radicalism, and more recently, global warming have risen as the world population increases.
In 1957, the Soviet Union launched the first artificial satellite into orbit and, soon afterward, Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space. Neil Armstrong, an American, was the first to set foot on another astronomical object, the Earth's Moon. Unmanned probes have been sent to all the major
planets in the solar system, with some (such as Voyager) in the process of leaving the solar system. The Soviet Union and the United States of America were the primary early leaders in space exploration in the 20th Century. Five space agencies, representing over fifteen countries,[90] have worked together to build the International Space Station. Aboard it, there has been a continuous human presence in space since 2000.[91]
See also
Timeline of the Big Bang
Geologic time scale
Timeline of evolution
Detailed logarithmic timeline
Natural history
History of the world
End of civilization
Timetable of the Precambrian
Geological history of Earth
External links
History of the Earth from
Detailed timeline
Note that Ma means "million years ago".
Hadean eon
3800 Ma
and earlier.
4533 Ma
The planet Earth and the planet Theia collide, sending countless moonlets into orbit around the young Earth. These moonlets eventually coalesce to form the Moon. The gravitational pull of the new Moon stabilises the Earth's fluctuating axis of rotation and sets up the conditions for the formation of life.[1]
4100 Ma
The surface of the Earth cools enough
for the crust to solidify. The atmosphere and the oceans form.[2]
Between 4500 and 2500 Ma
The earliest life appears, possibly derived from self-reproducing RNA molecules. The replication of these organisms requires resources like energy, space, and smaller building blocks, which soon
become limited, resulting in competition. Natural selection favours those molecules which are more efficient at replication. DNA molecules then take over as the main replicators. They soon develop inside enclosing membranes which provide a stable physical
and chemical environment conducive to their replication: proto-cells
3900 Ma
Late Heavy Bombardment: peak rate of impact events upon the inner planets by meteors. This constant disturbance probably obliterated any life that had already evolved, as the oceans boiled away completely; conversely, life may have been
transported to Earth by a meteor. [3]
Somewhere between 3900 - 2500 Ma
Cells resembling prokaryotes appear. These first organisms are chemoautotrophs: they use carbon dioxide as a carbon source and oxidize inorganic materials to extract energy. Later, prokaryotes evolve glycolysis, a set of chemical reactions that free the energy of organic molecules such as glucose. Glycolysis generates ATP molecules as short-term energy currency, and ATP continue to be used in almost all organisms, unchanged, to this day.
Archean eon
3800
Ma - 2500 Ma
|
Date |
Event |
|
3500 Ma |
Lifetime of the last universal ancestor; the split between the bacteria and the archaea occurs.
Bacteria develop primitive forms of
photosynthesis which at first do not produce oxygen. These organisms generate ATP by exploiting a proton gradient, a mechanism still used in virtually all organisms. |
|
3000 Ma |
Photosynthesizing cyanobacteria evolve; they use water as a reducing agent, thereby producing oxygen as waste product. The oxygen initially oxidizes dissolved iron in the oceans, creating iron ore. The oxygen concentration in the atmosphere subsequently rises, acting as a poison for many bacteria. The moon is still very
close to the earth and causes tides 1000 feet high. The earth is continually wracked by hurricane force winds. These extreme
mixing influences are thought to stimulate evolutionary processes. (See Oxygen Catastrophe) |
Proterozoic eon
2500
Ma - 542 Ma
Phanerozoic eon
542 Ma
- present
The Phanerozoic eon, literally the "period of well-displayed life", marks the appearance in the fossil record of abundant, shell-forming
organisms. It is subdivided into three eras, the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic, which are divided by major mass extinctions.
[edit]
Paleozoic
era
542 Ma
- 251.0 Ma
|
Date |
Event |
|
530 Ma |
The first known footprints on land date
to 530 Ma, indicating that early animal explorations may have predated the development of terrestrial plants.[5] |
|
475 Ma |
The first primitive plants move onto land,[6][citation needed] having evolved from green algae living along the edges of lakes.[7] They are accompanied by fungi, which may have aided the colonisation of land through symbiosis. |
|
363 Ma |
By the start of the Carboniferous period, the Earth begins to be recognisable. Insects roamed the land and would soon take to the skies; sharks predated the oceans,[8] and vegetation covered the land, with seed-bearing plants and forests soon to flourish.
Four-limbed tetrapods gradually gain adaptions which will help them occupy a terrestrial life-habit. |
|
251.4Ma |
The Permian-Triassic extinction event eliminates over 95% of species. This "clearing of the slate" may have led to an ensuing diversification. |
Mesozoic era
|
Date |
Event |
|
From 251.4 Ma |
The Mesozoic Marine Revolution begins: increasingly well-adapted and diverse predators pressurise sessile marine groups; the "balance of power" in the oceans
shifts dramatically as some groups of prey adapt more rapidly and effectively than others. |
|
220 Ma |
Eoraptor, an early dinosaur.
Gymnosperm forests dominate the land; herbivores grow to huge sizes in order to accommodate the large guts necessary to digest the nutrient-poor
plants.[citation needed] |
|
200 Ma |
The first accepted evidence for viruses - the group Geminiviridae at least exists.[9] Viruses are still poorly understood and may have arisen before "life" itself, or may be a more recent phenomenon. |
|
130 Ma |
The rise of the Angiosperms: These flowering plants boast structures that attract insects and other animals to spread pollen. This innovation causes a major burst of animal evolution through co-evolution. |
Cenozoic era
65.5
Ma – present

|

